Release 2 (9.0.2)
Part Number A92110-02
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle9i Application Server Globalization Support Guide Release 2 (9.0.2) Part Number A92110-02 |
|
This chapter describes the World-of-Books demo that is provided with Oracle9iAS.
This chapter contains the following topics:
The World-of-Books (WOB) demo demonstrates how to write a multilingual Web application and deploy it on the Oracle9iAS J2EE container. The application consists of the following Web sites:
The online bookstore is a multilingual Web application that interacts with customers. It allows customers to view books, check prices, and place orders. The application uses HTTP connections to send orders as XML documents to the suppliers. The online book supplier administration sites are Web applications that the book suppliers use to get orders from the bookstore, to send order status reports to the bookstore, and to notify the bookstore about newly available books.
The online bookstore supports 60 locales. Customers in these locales can use the online bookstore with their preferred language and cultural conventions. The online book supplier administration sites are in English only.
The WOB demo serves customers with different locale preferences. It is mainly written in Java, using Java Servlets, Java beans, and Java Server Pages (JSPs). It uses the Unicode capabilities available in Java, XML, JDBC, and the Oracle9i database to support multilingual data and a multilingual user interface.
This section contains the following topics:
Figure 4-1 shows the architecture of the WOB demo.
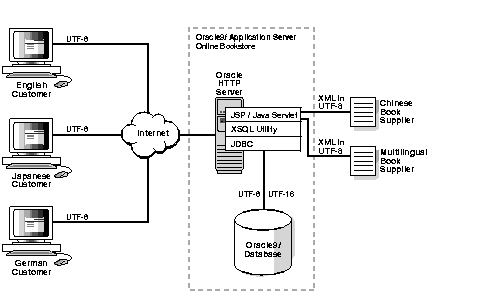
The application architecture can be summarized as follows:
CHAR datatype, or the data can be encoded in UTF-16 if the target column is of a SQL NCHAR datatype.
Figure 4-1 shows the WOB application on Oracle9iAS. The processing character set for the WOB application is UTF-16. The application uses XML messages to communicate with the Chinese book supplier and the multilingual book supplier. The XML messages are encoded in the UTF-8 character set. English, Japanese, and German customers connect to the WOB application through the Internet. The application serves all of the customers HTML pages encoded in the UTF-8 character set.
Table 4-1 shows the Java programs that contain most of the internationalization features for the WOB application. The programs are located in $WOB_HOME/src/oracle/wob2/wob.
The Language and Country classes are used only by the LocaleUtil class to represent a language and a country. The Localizer bean calls the LocaleUtil class for all static information about locale and character set, such as the default language and the default encoding used for the user interface of the bookstore. The LocaleUtil class reads the properties resource bundle, wob.properties, to initialize all static information for the online bookstore. The wob.properties file is located in $ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/demo/globalization/etc.
Most of the JSPs for the online bookstore include the header.jsp file, which uses the Localizer Java bean to keep locale information for a session. JSPs call the Localizer Java bean to perform all locale-sensitive operations such as formatting a date, encoding a URL, and converting HTML form parameters to Java strings. Some JSPs also call the LocaleUtil static class to get information such as the list of available languages and the list of currencies used for a specific country.
The programs for the World-of-Books demo are located $WOB_HOME, which is the WOB demo home directory defined as$ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/home/demo/globalization.
The database schema for the WOB demo consists of the following tables:
customers: Stores the user profile for each WOB user
books: Stores the information about each book
docs: Stores the content of each book so that customers can search the content of the books
Table 4-2 describes the customer table. When a registered user is logged in, the online bookstore uses the locale preferences in the customer table in the Localizer bean.
Table 4-3 describes the books table. The NVARCHAR2 datatype is used for the title, author, short description, and publisher of the book. By storing this information as Unicode in the NVARCHAR2 datatype, the WOB demo can support books in languages from around the world. The nsort column is used for queries about books so that the list is returned in an order appropriate for the locale.
Table 4-4 describes the docs table. It stores the contents of the books.
Indexes have been built for these tables. The following SQL files are used to create these tables and build the corresponding indexes. They are located in the $WOB_HOME/schema directory:
Oracle Text requires the language, format, cset, and doc columns of the docs table to build a full-text search index on the docs table. The ctxidx.sql and ctxsys.sql scripts are used to set up the full-text search index. They are located in $WOB_HOME/schema/ctx.
The source code and the build files of the World-of-Books demo are in the WOB demo home directory located in $WOB_HOME. Table 4-5 shows the directory structure under $WOB_HOME.
This section contains the following topics:
To build the WOB demo:
$ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/home/demo/globalization directory.
$WOB_HOME/etc directory.
JAVA_HOME and CLASSPATH environment variables. Oracle9iAS bundles JDK under$ORACLE_HOME/jdk so that you can use it for your JAVA_HOME.
You can also use your own JDK. For example:
% setenv ORACLE_HOME yourOracleHome % setenv JAVA_HOME $ORACLE_HOME/jdk % setenv J@EE_HOME $ORACLE_HOME/j2ee % copy $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib/xsul2.jar to $ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/home/lib
Make sure that $ORACLE_HOME/bin is in your path directory. For example:
% setenv PATH $ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH
TWO_TASK environment variable to point to your database. For example, if you can access the database from SQLPlus with the connect string iasdb, you can define the TWO_TASK environment variable as follows:
% setenv TWO_TASK iasdb
ANT command from the $WOB_HOME directory.
% ant
The build process performs the following tasks:
% ant setupctx
To deploy the WOB demo on Oracle9iAS J2EE:
ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/home/demo/globalization/j2ee_config/datasources.xml
<HOSTNAME> with the database server's hostname.
<PORT> with the database server's port number.
<ORACLE_SID> with the database server's Oracle SID.
After the data sources are added through Oracle Enterprise Manager, your J2EE_HOME/config/data-sources.xml file should contain entries that correspond to those in globalization/j2ee_config/data-sources.xml.
J2EE_HOME/demo/globalization/lib/g11n.ear through Oracle Enterprise Manager, or the dcmctl command utility as demonstrated below:
dcmctl deployApplication -file J2EE_HOME/demo/globalization/lib/g11n.ear -application g11n -component home
where home is the default OC4J instance onto which the demo is deployed.
Main site: http://<host>:<port>/g11n/imap.html
WOB site: http://<host>:<port>/g11n/wob/jsp/welcome.jsp
Supplier A: http://<host>:<port>/g11n/suppA/html/frame.html
Supplier B: http://<host>:<port>/g11n/suppB/html/frame.html
The online bookstore requires one of the following browsers:
The book supplier administration applications require Internet Explorer 5.0 or above.
To run the WOB demo, start the browser and enter the following URL:
http://host_name:7778/g11n/imap.html
You should see a screen similar to the following:
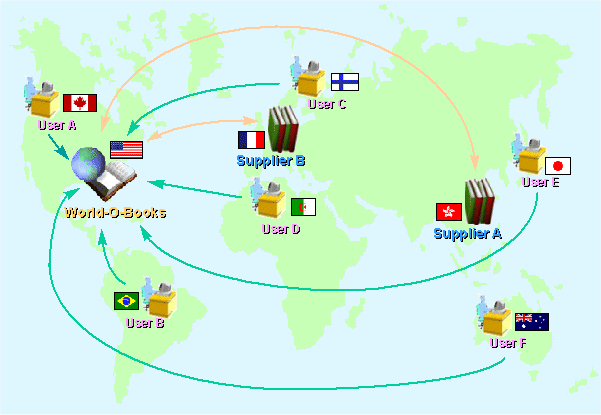
Select a link to start the desired application.
|
World-O-Books image: |
Online bookstore application |
|
Supplier A image: |
Chinese book supplier administration |
|
Supplier B image: |
Global book supplier administration |
You can navigate the online bookstore as a registered customer or as a visitor.
If you click the Supplier B image, the following screen appears:
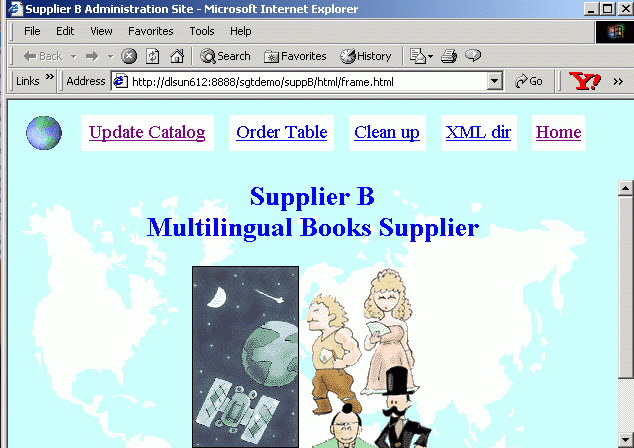
The links on the Supplier B administration site are as follows:
The World-of-Books online bookstore is fully aware of the user's locale. The application determines the user's locale and uses this locale to format dynamic HTML pages according to the user's language and cultural conventions.
This section contains the following topics:
The online bookstore determines the user's locale using three methods in the following order:
The Localizer bean has two properties, AcceptLang and localeOverride. The AcceptLang property indicates the Accept-Language header of the current HTTP request. The localeOverride property indicates whether a user has explicitly selected a locale, which is passed as a GET request parameter of the current HTTP request. The header.jsp file initializes the values of these properties as follows:
<jsp:useBean id="my" class="oracle.demo.wob2.wob.beans.Localizer" scope="session" /> <jsp:setProperty name="my" property="AcceptLang" value="<%=request.getHeader(\"Accept-Language\") %>" /> <jsp:setProperty name="my" property="localeOverride" value="<%= request.getParameter(\"v_override\") %>" />
This initialization causes the setAcceptLang() and setlocaleOverride() methods of the Localizer bean to initialize the Localizer associated with the current HTTP request with the appropriate locale information. The application determines the current user's locale as follows:
isLoggedIn() method of the Localizer determines whether the current user is logged in.
wob.properties resource bundle. This default locale is initialized in LocaleUtil.java.
The displayFlags() method in the Localizer generates the HTML content that enables users to enter a locale by clicking one of the displayed flags. The header.jsp file calls this method.
After the Localizer is initialized with the user's locale, all methods of the Localizer are sensitive to the locale. Table 4-6 shows examples of locale-sensitive methods defined in the Localizer.
Other locale-sensitive functions are described in the following sections.
The order in which books are listed in the result of a query is sensitive to the current user's locale. The search template is as follows:
SELECT books.bookid, langmap.language, books.title, books.author, substr(books.descpt, 1, 50) FROM books, langmap WHERE<specific search criteria>books.langid = langmap.langid AND nlssort(books.title, 'NLS_SORT = '|| books.nsort) IS NOT NULL ORDER BY langord(books.langid, 'Oracle_NLS_language'), nlssort(books.title, 'NLS_SORT='||books.nsort);
The langmap table maps language IDs to Oracle NLS language names and Oracle sort names used in the NLSSORT SQL function. The $WOB_HOME/schema/langmap.sql file creates the langmap table.
The SELECT statement orders the books with the ORDER BY clause as follows:
langord PL/SQL function returns. The langord function returns the smallest key value when the Oracle NLS language that corresponds to the current user's locale matches the language of the book. Thus the books are grouped so that the first group consists of books whose language corresponds to the user's locale.
NLSSORT SQL function returns. The NLSSORT function generates sort keys based on the linguistic order specified by the NLS_SORT parameter. The value of the NLS_SORT parameter is stored in the nsort column of the books table. Thus the books in the sorted group are ordered by the Oracle sort sequence name stored in the nsort column.
The application also orders lists in the user interface using locale information. For example, it uses the displayLanguageOptions() method of the Localizer bean to construct a list of languages so users can select a language. The displayLanguageOptions() method collates the languages in the list based on the locale-specific Java collator. This collator is constructed using the current locale represented by the Localizer bean. The following code gets the collation key of each language name in the current user's locale:
String[] languages = localeutil.getSupportedLanguagesArray(); CollationKey[] keys = new CollationKey[languages.length]; for (int i = 0; i < languages.length; i++) { keys[i] = collator.getCollationKey(getMessage(languages[i]) + " [" + languages[i]); }
After the keys array is filled with collation keys, the array is sorted based on the binary value of each key. The other methods that collate drop-down lists are displayCountryOptions(), displayCurrencyOptions(), and displayScriptCountryVars().
The online bookstore allows users to search the contents of books in a locale-sensitive manner. The following query searches the contents of the books from the docs table:
SELECT books.bookid, langmap.language, books.title, books.author, substr(books.descpt, 1, 50) FROM books, langmap, docs WHERE contains(docs.doc, 'search_key', 0) > 0 AND books.langid = langmap.langid AND nlssort(books.title, 'NLS_SORT = '|| books.nsort) IS NOT NULL ORDER BY langord(books.langid, 'Oracle_NLS_language'), nlssort(books.title, 'NLS_SORT='||books.nsort);
The contains(docs.doc, 'search_key', 0) function in the WHERE clause returns a positive value when the search key is found in the contents of a document stored in the doc column of the docs table. The rest of the query is similar to the query used for the book search.
Oracle Text by default uses the language of the search key as defined by the NLS_LANGUAGE session parameter. To conduct the search in a language-sensitive manner, search.jsp issues an ALTER SESSION statement to change the value of the NLS_LANGUAGE parameter to the value that the user specifies before submitting the content search query. The ALTER SESSION statement is as follows:
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_LANGUAGE=language;
Calling the getParameter("v_language") method of the HTTPServletRequest object obtains the language value, where v_language is a form input parameter from the advanced search screen.
In the online bookstore, an attribute of the Localizer bean stores the encoding used for HTML pages. The default_encoding property of the wob.properties resource bundle initializes the attribute with the default page encoding. By default, the online bookstore uses UTF-8 as the HTML page encoding to provide support for multilingual content.
To enforce UTF-8 as the page encoding in JSPs, define the appropriate Content-Type header. For the online bookstore, put the Content-Type page directive into header.jsp as follows:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
You only need to put this directive into header.jsp because all other JSPs that produce HTML output include header.jsp.
The online bookstore allows users to override the default encoding with the preferred encoding from the user profile. The user can choose a preferred page encoding from the user profile modification page. After the user logs in, the encoding attribute of the current Localizer bean is updated to the preferred encoding. To set the encoding in JSPs, header.jsp checks whether the user has logged in and calls the HTTPServletResponse.setContentType() method to overwrite the Content-Type header defined in the JSP page directive with the preferred encoding. The code is as follows:
<% if (my.isLoggedIn()) response.setContentType("text/html; charset=" + my.getEncoding()); %>
The getEncoding() method of the Localizer bean (my) returns the preferred encoding from the current user's profile.
The online bookstore accepts multilingual text as HTML form input. The input can be a search key when the user wants to search for a book, or it can be a user name at login. The browser sends form input as a sequence of bytes in the same encoding as the HTML form. Converting the input to Java strings encoded as Unicode requires the page encoding information. Because the page encoding is stored as an attribute of the Localizer, the conversion function is encapsulated in the Localizer class.
The translateParameter() method of the Localizer bean converts form input from the encoding indicated in the encoding attribute of the bean to a Java string. The method is as follows:
public String translateParameter(parameter_string)
{
try {
byte[] paramBytes = param.getBytes("ISO-8859-1");
return new String(paramBytes, getEncoding());
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e)
{
// return the same string if exception
}
return param;
}
The getEncoding() method of the Localizer bean returns the page encoding for HTML forms.
The JSPs call the translateParameter() method where form input is processed. For example, the following files call this method:
All URLs that are embedded in an HTML page must be encoded. They must use the same encoding as the HTML page. The Localizer bean is the best place to encapsulate the encodeURL() method. This method encodes a URL according to the encoding attribute of the Localizer.
The following JSPs call the encodeURL() method:
All embedded URLs for the online bookstore are encoded in ASCII and do not need to be encoded. The encodeURL() method is called to illustrate the concept of encoding URLs.
The online bookstore uses the following locale-sensitive text formatting elements for HTML pages:
To support multiple locales simultaneously, the online bookstore externalizes these elements to a locale-specific cascading style sheet (CSS) instead of hard-coding them in JSPs. The CSS file structure is the same as the static HTML file structure for the WOB online help. The CSS files are as follows:
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/css/style.css (the default CSS)
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/css/ar/style.css
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/css/he/style.css
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/css/iw/style.css
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/css/ja/style.css
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/css/zh/style.css
In $WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/jsp/header.jsp, the getLocalizedURL() method of the Localizer bean gets the full path of the CSS that corresponds to the current locale. If there is no CSS that is specific to the locale, then the application uses the default CSS.
The following is the CSS for Arabic text:
html { direction: rtl } h3 { font-size: 100%; text-align: end; font-weight: bold; color: #FFFFFF }
The Arabic CSS defines the writing direction of the HTML page as right to left (RTL). The text is always aligned to the end of the writing direction.
The following is the CSS for Japanese text:
html { direction: ltr } h3 { font-size: 100%; text-align: end; font-family: "MS Gothic", "MS Mincho", "Times New Roman"... font-weight: bold; color: #FFFFFF } tr { font-family: "MS Gothic", "MS Mincho", "Times New Roman",... font-size: 12pt; } p { font-family: "MS Gothic", "MS Mincho" "Times New Roman",... font-size: 12pt}
The Japanese CSS defines the writing direction as left to right (LTR). The text is aligned to the end of the writing direction. The font families that are used for displaying Japanese text are MS Gothic and MS Mincho. These are Japanese Microsoft Windows fonts. If you do not specify the font family in the CSS, then the application uses the default font of the browser.
The WOB demo uses the Oracle JDBC driver to access an Oracle9i database. The JDBC driver transparently converts the data stored in the database to and from Java strings. No special handling is necessary to access Unicode data stored in the database in most cases.
There is one case in which you need special data handling. When a Java string is bound to a column of the NVARCHAR datatype in an INSERT or UPDATE SQL statement, you should call the setFormOfUse() method of the OraclePreparedStatement class to tell JDBC that the target column is of the NVARCHAR datatype. The setFormOfUse() method is called in $WOB_HOME/src/orcalc/demo/wob2/supp/beans/insertItem.java when a new book is inserted into the books table.
The online bookstore consists of the following translatable content:
This section contains the following topics:
The static HTML files for the WOB online help are located in $ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/demo/globalization/docroot/wob/help. The English version of the online help is stored at the top level of the help directory. The translated help for each locale is stored in the corresponding help/locale_name directory. For example, the Japanese online help is stored in the help/ja_JP directory.
The current user's locale determines which help subdirectory the application uses. The Localizer bean stores the user's current locale. The getLocalizedURL() method returns the correct path of an HTML file that corresponds to the user's locale. Given the relative help path of ../help/index.html and the current locale of ja_JP, this method checks for existence of the following files in the order they are listed and returns the first one it finds:
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/help/ja_JP/index.html
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/help/ja/index.html
$WOB_HOME/docroot/wob/help/index.html
The header.jsp file calls this method to get the correct path for every translated HTML file and uses the result to construct the HREF tag to reference the appropriate online help.
A list resource bundle stores all translatable messages that comprise the online bookstore user interface. The resource bundle is located in $ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/demo/globalization/src/oracle/demo/wob2/wob. This resource bundle is translated into 27 languages, and the translated resource bundle names have suffixes that correspond to the Java locale name.
/resource/MessageBundle.java
The getMessage() method of the Localizer bean gets a translated message from the resource bundle that corresponds to the current locale. Most JSPs call this method.
|
|
 Copyright © 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|