Operations on Strings¶
Concatenation (+ and *)¶
(ch08_add)
Indexing with ([])¶
The indexing operator selects a single character from a string.
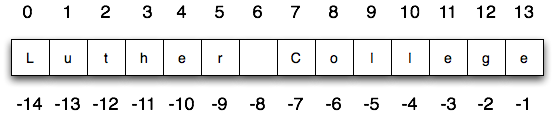
It is also the case that the positions are named from right to left using negative numbers where -1 is the rightmost index and so on.
(chp08_index1)
For loop traversal (for)¶
Traversing a string means accessing each character in the string, one at a time. For example, the following for loop:
for ix in 'Example':
...
executes the body of the loop 7 times with different values of ix each time.
Length¶
The len function, when applied to a string, returns the number of characters in a string.
Example: len('happy') evaluates to 5.
(chp08_len2)
Slice¶
A substring of a string is called a slice. The slice operator [n:m] returns the part of the string from the n’th character
to the m’th character, including the first but excluding the last.
(chp08_slice1)
String Comparison (>, <, >=, <=, ==, !=)¶
The six common comparision operators work with strings, evaluating according to lexigraphical order. Examples:
'apple' < 'banana'evaluates toTrue.'Zeta' < 'Appricot'evaluates toFalse.'Zebra' <= 'aardvark'evaluates toTruebecause all upper case letters precede lower case letters.
in and not in operator (in, not in)¶
The in operator tests whether one string is contained inside another string.
Examples:
'heck' in "I'll be checking for you."evaluates toTrue.'cheese' in "I'll be checking for you."evaluates toFalse.
(chp08_slice1)