| Oracle® Database Heterogeneous Connectivity Administrator's Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14232-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Heterogeneous Connectivity Administrator's Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14232-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes the configuration and usage of Generic Connectivity agents.
This chapter contains these topics:
Generic Connectivity is intended for low-end data integration solutions requiring the ad hoc query capability to connect from an Oracle database server to non-Oracle database systems.
Generic Connectivity is implemented as either a Heterogeneous Services ODBC agent or a Heterogeneous Services OLE DB agent. An ODBC agent and an OLE DB agent are included as part of your Oracle system. ODBC agents are supported on Solaris, HP-UX, AIX, Windows, and Linux (x86) 32-Bit platforms. OLE DB agents are supported only on the Windows platform.
Any data source compatible with the ODBC or OLE DB standards described in this chapter can be accessed using a Generic Connectivity agent.
This section contains the following topics:
Generic Connectivity is implemented as one of the following types of Heterogeneous Services agents:
ODBC agent for accessing ODBC data providers
OLE DB agent for accessing OLE DB data providers that support SQL processing—sometimes referred to as OLE DB (SQL)
OLE DB agent for accessing OLE DB data providers without SQL processing support—sometimes referred to as OLE DB (FS)
Each user session receives its own dedicated agent process spawned by the first use in that user session of the database link to the non-Oracle system. The agent process ends when the user session ends.
To access the non-Oracle data store using Generic Connectivity, the agents work with an ODBC or OLE DB driver. The Generic Connectivity agent provides support for the ODBC or OLE DB driver interface. The driver that you use must be on the same platform as the agent. The non-Oracle data stores can reside on the same machine as the Oracle database server or on a different machine.
Figure 7-1 shows an example of a configuration in which an Oracle and non-Oracle database are on separate machines, communicating through a Heterogeneous Services ODBC agent.
Figure 7-1 Oracle and Non-Oracle Systems on a Separate Machines
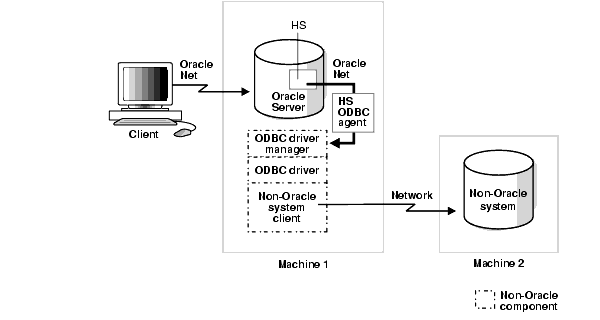
In this configuration:
A client connects to the Oracle database server through Oracle Net.
The Heterogeneous Services component of the Oracle database server connects through Oracle Net to the Heterogeneous Services ODBC agent.
The agent communicates with the following non-Oracle components:
An ODBC driver manager
An ODBC driver
A non-Oracle client application
This client connects to the non-Oracle data store through a network.
Figure 7-2 shows an example of a configuration in which an Oracle and non-Oracle database are on the same machine, again communicating through a Heterogeneous Services ODBC agent.
Figure 7-2 Oracle and Non-Oracle Systems on the Same Machine

In this configuration:
A client connects to the Oracle database server through Oracle Net.
The Heterogeneous Services component of the Oracle database server connects through Oracle Net to the Heterogeneous Services ODBC agent.
The agent communicates with the following non-Oracle components:
An ODBC driver manager
An ODBC driver
The driver then allows access to the non-Oracle data store.
Note:
The ODBC driver may require non-Oracle client libraries even if the non-Oracle database is located on the same machine. Refer to your ODBC driver documentation for information about the requirements for the ODBC driver.SQL statements that are sent using a Generic Connectivity agent are executed differently depending on the type of agent you are using: ODBC, OLE DB (SQL), or OLE DB (FS). For example, if a SQL statement involving tables is sent using an ODBC agent for a file-based storage system, the file can be manipulated as if it were a table in a relational database. The naming conventions used at the non-Oracle system can also depend on whether you are using an ODBC or OLE DB agent.
The Heterogeneous Services and Generic Connectivity agent maps the data types used in ODBC-compliant and OLE DB-compliant data sources to supported Oracle data types. When the results of a query are returned, the Oracle database server converts the ODBC or OLE DB data types to Oracle data types. For example, the ODBC data type SQL_TIMESTAMP and the OLE DB data type DBTYPE_DBTIMESTAMP are converted to Oracle's DATE data type.
If a table contains a column whose data type is not supported by Generic Connectivity, the column information is not returned to the Oracle server.
Generic Connectivity restrictions include:
A table including a BLOB column must have a separate column that serves as a primary key.
BLOB and CLOB data cannot be read by passthrough queries.
Updates or deletes that include unsupported functions within a WHERE clause are not allowed.
Generic Connectivity does not support stored procedures.
Generic Connectivity agents cannot participate in distributed transactions; they support single-site transactions only.
Generic Connectivity does not support multithreaded agents.
Updating LONG columns with bind variables is not supported.
Generic Connectivity does not support rowids.
Generic Connectivity supports the following statements, but only if the ODBC or OLE DB driver and non-Oracle system can execute them and if the statements contain supported Oracle SQL functions:
DELETE
INSERT
SELECT
UPDATE
Only a limited set of functions are assumed to be supported by the non-Oracle system. Most Oracle functions have no equivalent function in this limited set. Consequently, although post-processing is performed by the Oracle database server, many Oracle functions are not supported by Generic Connectivity, possibly impacting performance.
If an Oracle SQL function is not supported by Generic Connectivity, this function is not supported in DELETE, INSERT, or UPDATE statements. In SELECT statements, these functions are evaluated by the Oracle database server and processed after they are returned from the non-Oracle system.
If an unsupported function is used in a DELETE, INSERT, or UPDATE statement, it generates the following Oracle error:
ORA-02070: database db_link_name does not support function in this context
Generic Connectivity assumes that the following minimum set of SQL functions is supported by the ODBC driver or OLE DB provider that is being used:
AVG(exp)
LIKE(exp)
COUNT(*)
MAX(exp)
MIN(exp)
NOT
To implement Generic Connectivity on a non-Oracle data source, you must set the agent parameters.
This section contains the following topics:
Setting Initialization Parameters for an ODBC-Based Data Source
Setting Initialization Parameters for an OLE DB-Based Data Source
You must create and customize an initialization file for your Generic Connectivity agent. Oracle supplies sample initialization files, inithsodbc.ora for ODBC agents and inithsoledb.ora for OLE DB agents. The sample files are stored in the $ORACLE_HOME/hs/admin directory.
To create an initialization file for an ODBC or OLE DB agent, copy the applicable sample initialization file and rename the file to initsid.ora, where sid is the system identifier you want to use for the instance of the non-Oracle system to which the agent connects.
The sid is also used to identify how to connect to the agent when you configure the listener by modifying the listener.ora file. The sid that you add to the listener.ora file must match the sid in an initsid.ora file, because the agent spawned by the listener searches for a matching initsid.ora file. When you copy and rename the initsid.ora file, ensure that it remains in the $ORACLE_HOME/hs/admin directory.
Customize the initsid.ora file by setting the parameter values used for Generic Connectivity agents to values appropriate for your system, agent, and drivers. You must edit the initsid.ora file to change the HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO initialization parameter. The HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO initialization parameter specifies the information required for connecting to the non-Oracle system.
See Also:
Section 4.2, "Setting Initialization Parameters" for more information about parametersSet the parameter values as follows:
[SET][PRIVATE] parameter=value
SET and PRIVATE are optional keywords. If you do not specify either SET or PRIVATE, the parameter is used only as an initialization parameter for the agent.
SET specifies that, in addition to being used as an initialization parameter, the parameter value is set as an environment variable for the agent process.
PRIVATE specifies that the parameter value is private and not transferred to the Oracle database server. It does not appear in dynamic performance views or in graphical user interfaces.
SET PRIVATE specifies that the parameter value is set as an environment variable for the agent process and is also private (not transferred to the Oracle database server, not appearing in dynamic performance views or graphical user interfaces).
parameter is the Heterogeneous Services initialization parameter that you are specifying. See Section 4.2, "Setting Initialization Parameters" for a description of all Heterogeneous Services parameters. The parameter is case-sensitive.
value is the value you want to specify for the Heterogeneous Services parameter. The value is case-sensitive.
For example, to enable tracing for an agent, set the HS_FDS_TRACE_LEVEL initialization parameter as follows:
HS_FDS_TRACE_LEVEL=ON
Most parameters are needed only as initialization parameters, so you usually do not need to use the SET or PRIVATE keywords. Use SET for parameter values that the drivers or non-Oracle system need as environment variables.
PRIVATE is supported only for the following Heterogeneous Services initialization parameters:
HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO
HS_FDS_SHAREABLE_NAME
HS_FDS_TRACE_LEVEL
Use PRIVATE for these initialization parameters only if the parameter value includes sensitive information such as a username or password.
The settings for the initialization parameters vary depending on the type of operating system.
Specify a file data source name (DSN) or a system DSN which has previously been defined using the ODBC Driver Manager.
Specify the value as follows:
HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO=dsn
Assume that a system DSN has been defined in the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator. In order to connect to this SQL Server database through the gateway, the following line is required in the initsid.ora file:
HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO=sqlserver7
sqlserver7 is the name of the system DSN defined in the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator.
The following procedure enables you to define a system DSN in the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator, version 3.5:
From the Start menu, choose Settings > Control Panel and select ODBC .
Select the system DSN tab page to display the system data sources.
Click Add.
From the list of installed ODBC drivers, select the name of the driver that the data source will use. For example, select SQL Server.
Click Finish.
Enter a name for the DSN and an optional description. Enter other information depending on the ODBC driver. For example, for SQL Server enter the SQL Server machine name.
Note:
The name entered for the DSN must match the value of the initialization parameterHS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO that is specified in initsid.ora.Refer to your ODBC driver documentation and follow the prompts to complete configuration of the DSN.
After creating the system DSN, click OK to exit the ODBC Data Source Administrator.
Specify a DSN and the path of the ODBC shareable library, as follows:
HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO=dsn_value HS_FDS_SHAREABLE_NAME=full_path_of_odbc_driver
The HS_FDS_SHAREABLE_NAME initialization parameter should point to the location of the ODBC driver manager and not to the ODBC driver.
The HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO initialization parameter is required for all platforms for an ODBC agent. The HS_FDS_SHAREABLE_NAME initialization parameter is required on UNIX platforms for an ODBC agent. Other initialization parameters have defaults or are optional. You can use the default values and omit the optional parameters, or you can specify the parameters with values tailored for your installation.
Note:
Before deciding whether to accept the default values or to change them, see Appendix A for detailed information about all the initialization parameters.The following is an example of an odbc.ini file that uses DataDirect Technologies SQLServer ODBC driver:
[ODBC Data Sources] SQLServerWP=DataDirect 4.10 SQL Server Wire Protocol [SQLServerWP] Driver=/opt/odbc410/lib/ivmsss18.so Description=DataDirect 4.10 SQL Server Wire Protocol Database=oratst LogonID=TKHOUSER Password=TKHOUSER Address=sqlserver-pc,1433 QuotedId=No AnsiNPW=No [ODBC] Trace=0 TraceFile=/opt/odbc410/odbctrace.out TraceDll=/opt/odbc410/lib/odbctrac.so InstallDir=/opt/odbc410 ConversionTableLocation=/opt/odbc410/tables UseCursorLib=0
To configure the Generic Connectivity ODBC agent to use this driver, the following lines are required in initsid.ora:
HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO=SQLServerWP HS_FDS_SHAREABLE_NAME=/opt/odbc4/lib/libodbc.so set ODBCINI=/opt/odbc/odbc.ini
Note that the set statements are optional as long as they are specified in the environment where the listener was started. Each database has its own set statements.
The HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO initialization parameter value must match the ODBC data source name in the odbc.ini file.
You can set these parameters only on the Windows platform.
Specify a data link (UDL) that has previously been defined:
SET|PRIVATE|SET PRIVATE HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO="UDLFILE=data_link"
Note:
If the parameter value includes an equal sign (=), then it must be surrounded by quotation marks.The HS_FDS_CONNECT_INFO initialization parameter is required for an OLE DB agent. Other initialization parameters have defaults or are optional. You can use the default values and omit the optional parameters, or you can specify the parameters with values that are customized for your installation.
Note:
Before deciding whether to accept the default values or to change them, see Appendix A for detailed information about all the initialization parameters.To use an ODBC agent, you must have an ODBC driver installed on the same machine as the Oracle database server. On UNIX, you must have an ODBC driver manager available on the same machine. The ODBC driver manager and driver must meet the following requirements:
The ODBC driver (and the non-Oracle system) must support a minimum transaction isolation level of read committed.
On Windows machines, the 32-bit ODBC driver must have compliance level to ODBC standard 2.5.
On Windows machines, the ODBC driver and driver manager must conform to ODBC application program interface (API) conformance Level 1 or higher. If the ODBC driver or driver manager does not support multiple active ODBC cursors, the complexity of SQL statements that you can execute using Generic Connectivity is restricted.
On UNIX machines, the ODBC driver must be 32-bit and must have compliance level to ODBC Standard 2.5 and have a conformance level 1 or higher. If the ODBC driver works with an ODBC driver manager, the ODBC driver manager must be compliant with ODBC Standard 2.5 or higher.
See Also:
Your ODBC driver documentation for dependencies on an ODBC driver manager, and Oracle Database Conceptsfor more information on transaction isolation levels.The ODBC driver you use must support all of the core SQL ODBC data types and must support SQL grammar level SQL_92. The ODBC driver should also expose the following ODBC APIs shown in Table 7-1:
Table 7-1 ODBC Functions
| ODBC Function | Comment |
|---|---|
SQLAllocConnect |
- |
SQLAllocEnv |
- |
SQLAllocStmt |
- |
SQLBindCol |
- |
SQLBindParameter |
- |
SQLColumns |
- |
SQLConnect |
- |
SQLDescribeCol |
- |
SQLDisconnect |
- |
SQLDriverConnect |
- |
SQLError |
- |
SQLExecDirect |
- |
SQLExecute |
- |
SQLExtendedFetch |
Recommended if used by the non-Oracle system. |
SQLFetch |
- |
SQLForeignKeys |
Recommended if used by the non-Oracle system. |
SQLFreeConnect |
- |
SQLFreeEnv |
- |
SQLFreeStmt |
- |
SQLGetConnectOption |
- |
SQLGetData |
- |
SQLGetFunctions |
- |
SQLGetInfo |
- |
SQLGetTypeInfo |
- |
SQLNumParams |
Recommended if used by the non-Oracle system. |
SQLNumResultCols |
- |
SQLParamData |
- |
SQLPrepare |
- |
SQLPrimaryKeys |
Recommended if used by the non-Oracle system. |
SQLProcedureColumns |
Recommended if used by the non-Oracle system. |
SQLProcedures |
Recommended if used by the non-Oracle system. |
SQLPutData |
- |
SQLRowCount |
- |
SQLSetConnectOption |
- |
SQLSetStmtOption |
- |
SQLStatistics |
- |
SQLTables |
- |
SQLTransact |
Recommended if used by the non-Oracle system. |
These requirements apply to OLE DB data providers that have a SQL processing capability and expose the OLE DB interfaces.
Generic Connectivity passes the username and password to the provider when calling IDBInitialize::Initialize().
OLE DB (SQL) connectivity requires that the data provider expose the following OLE DB interfaces shown in Table 7-2:
Table 7-2 OLE DB (SQL) Interfaces
| Interface | Methods | Notes |
|---|---|---|
IAccessor |
CreateAccessor, ReleaseAccessor |
- |
IColumnsInfo |
GetColumnsInfo (Command and Rowset objects) |
- |
ICommand |
Execute |
- |
ICommandPrepare |
Prepare |
- |
ICommandProperties |
SetProperties |
- |
ICommandText |
SetCommandText |
- |
ICommandWithParameters |
GetParameterInfo |
- |
IDBCreateCommand |
CreateCommand |
- |
IDBCreateSession |
CreateSession |
- |
IDBInitialize |
Initialize |
- |
IDBSchemaRowset |
GetRowset (tables, columns, indexes; optionally also procedures, procedure parameters) |
- |
IErrorInfo |
GetDescription, GetSource |
You can also use IErrorLookup with the GetErrorDescription method. |
IErrorRecords |
GetErrorInfo |
- |
ILockBytes (OLE) |
Flush, ReadAt, SetSize, Stat, WriteAt |
Required only if BLOB data types are used in the OLE DB provider. |
IRowset |
GetData, GetNextRows, ReleaseRows, RestartPosition |
- |
IStream (OLE) |
Read, Seek, SetSize, Stat, Write |
- |
ISupportErrorInfo |
InterfaceSupportsErrorInfo |
- |
ITransactionLocal (optional) |
StartTransaction, Commit, Abort |
- |
These requirements apply to OLE DB data providers that do not have SQL processing capabilities. If the provider exposes them, OLE DB (FS) connectivity also uses OLE DB Index interfaces.
OLE DB (FS) connectivity requires that the data provider expose the following OLE DB interfaces shown in Table 7-3:
Table 7-3 OLE DB (FS) Interfaces
| Interface | Methods | Notes |
|---|---|---|
IAccessor |
CreateAccessor, ReleaseAccessor |
- |
IColumnsInfo |
GetColumnsInfo (Command and Rowset objects) |
- |
IOpenRowset |
OpenRowset |
- |
IDBCreateSession |
CreateSession |
- |
IRowsetChange |
DeleteRows, SetData, InsertRow |
- |
IRowsetLocate |
GetRowsByBookmark |
- |
IRowsetUpdate |
Update (optional) |
- |
IDBInitialize |
Initialize, Uninitialize |
- |
IDBSchemaRowset |
GetRowset (tables, columns, indexes; optionally also procedures, procedure parameters) |
- |
ILockBytes (OLE) |
Flush, ReadAt, SetSize, Stat, WriteAt |
Required only if BLOB data types are used in the OLE DB provider |
IRowsetIndex |
SetRange |
Required only if indexes are used in the OLE DB provider |
IErrorInfo |
GetDescription, GetSource |
You can use IErrorLookup with the GetErrorDescription method as well. |
IErrorRecords |
GetErrorInfo |
- |
IRowset |
GetData, GetNextRows, ReleaseRows, RestartPosition |
- |
IStream (OLE) |
Read, Seek, SetSize, Stat, Write |
- |
ITransactionLocal (optional) |
StartTransaction, Commit, Abort |
- |
ISupportErrorInfo |
InterfaceSupportsErrorInfo |
- |
ITableDefinition |
CreateTable, DropTable |
- |
IDBProperties |
SetProperties |
- |
Because OLE DB (FS) connectivity is generic, it can connect to a number of different data providers that expose OLE DB interfaces. Every such data provider must meet the certain requirements.
Note:
The data provider must expose bookmarks. This enables tables to be updated. Without bookmarks being exposed, the tables are read-only.The OLE DB data source must support the following initialization properties:
DBPROP_INIT_DATASOURCE
DBPROP_AUTH_USERID
Note:
Required if the user ID has been supplied in the security fileDBPROP_AUTH_PASSWORD
Note:
Required if the user ID and password have been supplied in the security fileThe OLE DB data source must also support the following rowset properties:
DBPROP_IRowsetChange = TRUE
DBPROP_UPDATABILITY = CHANGE+DELETE+INSERT
DBPROP_OWNUPDATEDELETE = TRUE
DBPROP_OWNINSERT = TRUE
DBPROP_OTHERUPDATEDELETE = TRUE
DBPROP_CANSCROLLBACKWARDS = TRUE
DBPROP_IRowsetLocate = TRUE
DBPROP_OTHERINSERT = FALSE